本地英文版地址: ../en/windows.html
此功能目前处于 beta 测试阶段,可能会有变化。 设计和代码不如官方的 GA 功能成熟,而且是按原样提供的,没有保障。 Beta版特性不受官方 GA 特性的 SLA 支持。
msi 安装包适合在 Windows 上安装 Elasticsearch。
这可以将 Elasticsearch 安装为 Windows 服务,或者允许使用内含的可执行文件 elasticsearch.exe手动运行之。
Elasticsearch 历史上一直使用 .zip 存档安装。
如果你愿意,你可以继续使用 .zip 方法。
此软件包可在 Elastic 许可下免费使用。 它包含开放源码和免费的商业特性,并能访问付费商业特性。 开始为期30天的试用 尝试使用付费的商业特性。 有关 Elastic 许可等级的更多信息,请参考 订阅(Subscriptions) 页面。
在Windows上,Elasticsearch 的机器学习特性需要 Microsoft Universal C Runtime 库。 这个库内置在 Windows10, Windows Server 2016 以及更近期的Windows版本。 对于更老版本的Windows,可以通过 Windows Update安装,或者 单独下载 页面。 如果你无法安装 Microsoft Universal C Runtime 库,只要你停用机器学习特性,你仍然可以使用Elasticsearch的其他功能。
Elasticsearch 最新的稳定版本可以在 下载 Elasticsearch 页面找到。 其他版本可以在 过去发布的版本(Past Releases) 页面上找到。
从 https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.7.1.msi 下载 lasticsearch v7.7.1 版本的 .msi 安装包。
双击下载的 .msi 安装包来启动一个 GUI 向导,该向导将指导你完成安装过程。
你可以单击 ? 按钮,它会显示一个侧面板,其中包含每个输入的附加信息:
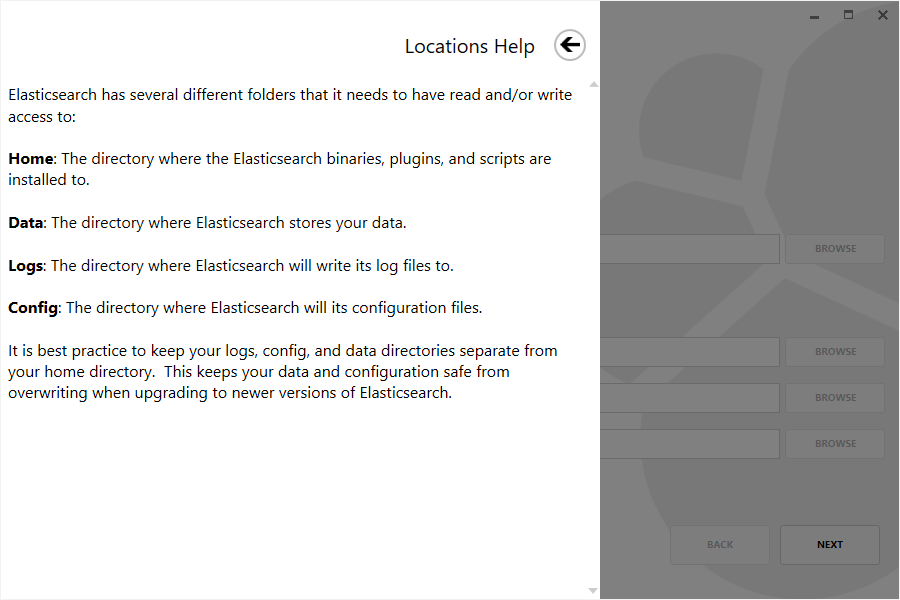
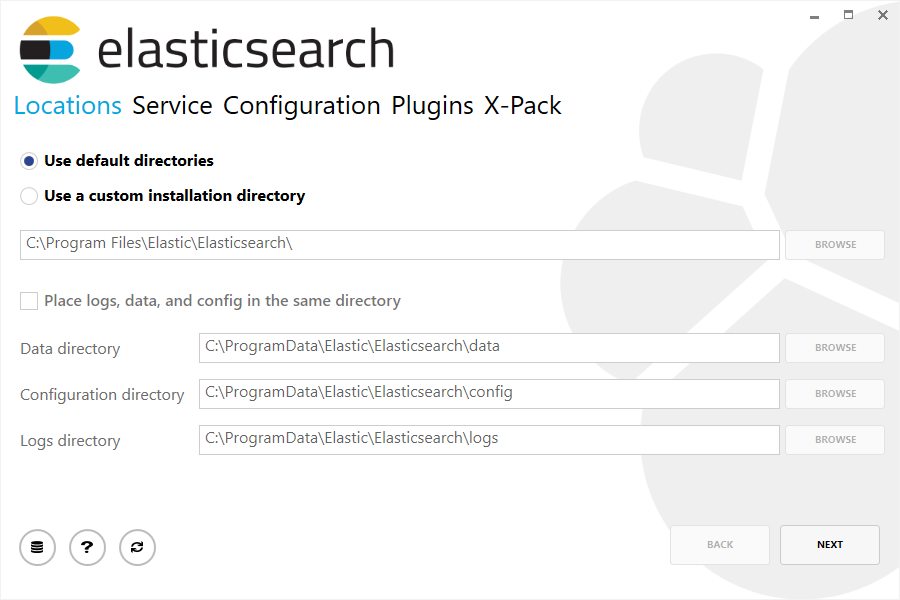
在第一屏中,选择安装目录。 此外,选择放置数据、日志和配置的目录,或 使用默认位置:
然后根据需要选择是安装为服务还是手动启动 Elasticsearch。 作为服务安装时,你还可以设置运行服务的 Windows 帐户、服务是否应在安装后启动,以及随 Windows 启动:
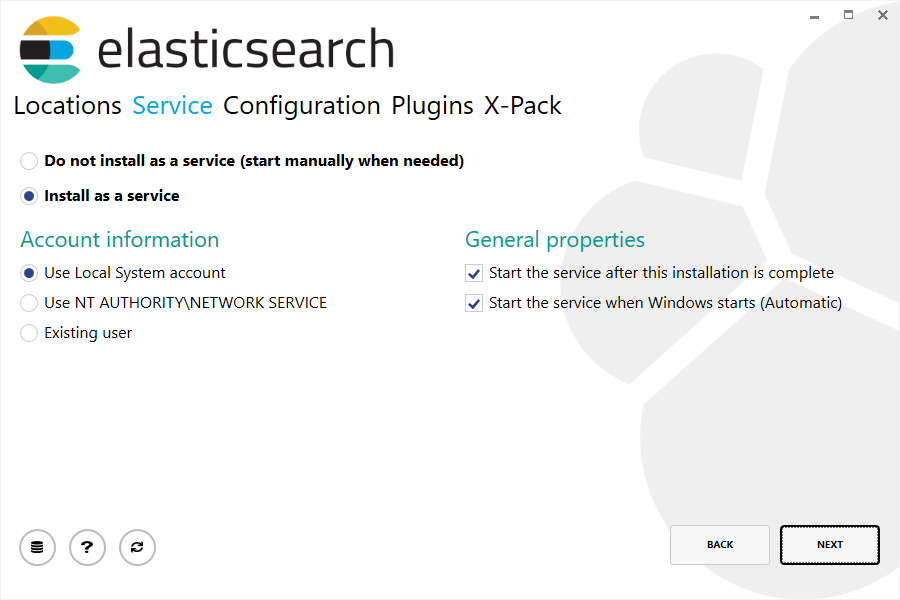
选择运行服务的 Windows 帐户时,请确保所选帐户有足够的权限访问所选的安装目录和其他部署目录。 还要确保该帐户能够运行 Windows 服务。
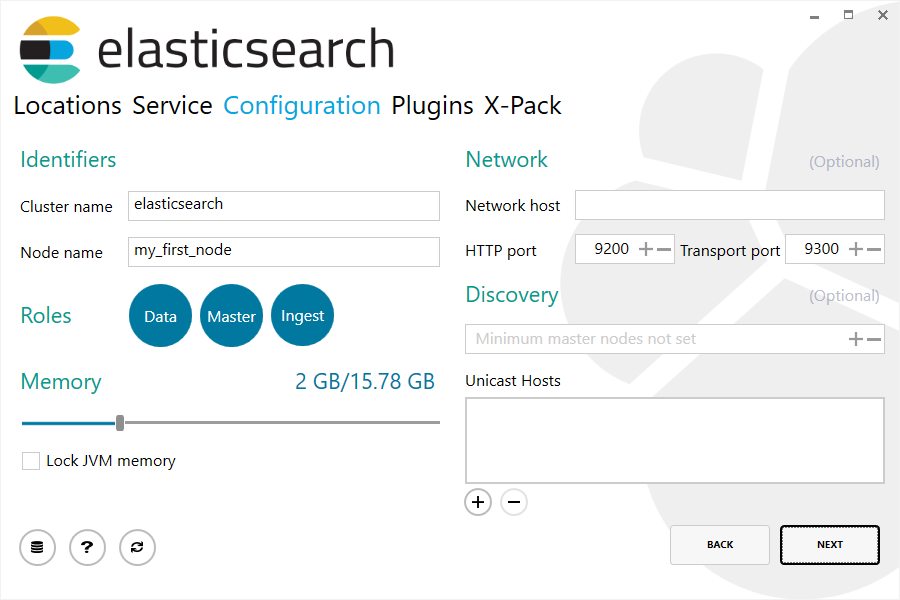
常见配置设置显示在 Configuration 部分,除了内存和网络设置之外,还允许设置集群名称、节点名称和角色:
作为安装的一部分,提供了一个可以下载和安装的常见插件列表,可以选择配置一个 HTTPS 代理来下载这些插件。
确保安装机器可以访问互联网,并且公司的任意一个防火墙都配置为允许从 artifacts.elastic.co 下载:
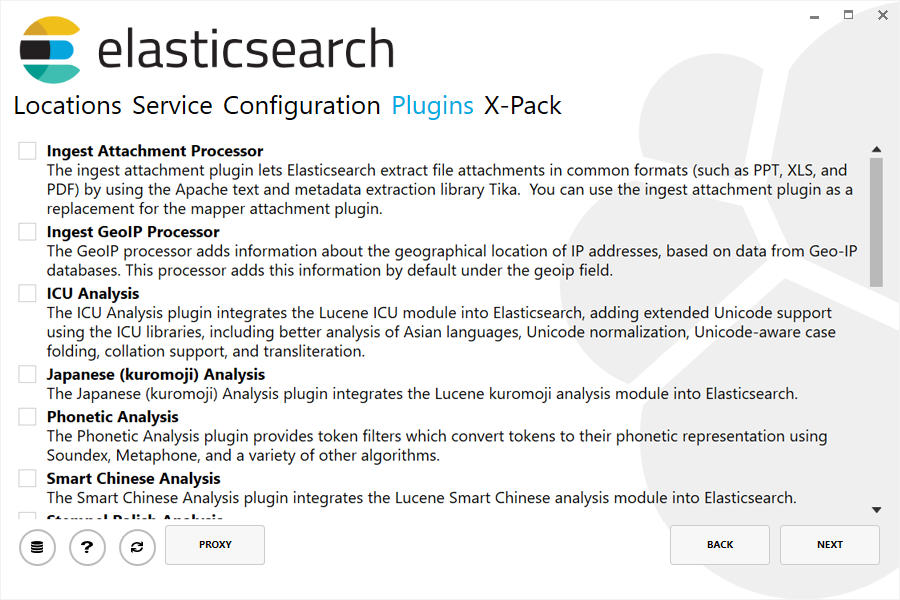
从 6.3.0 版本开始,X-Pack 是 默认安装 的。 除了安全配置和内置用户配置之外,最后一步允许选择要安装的许可证类型:
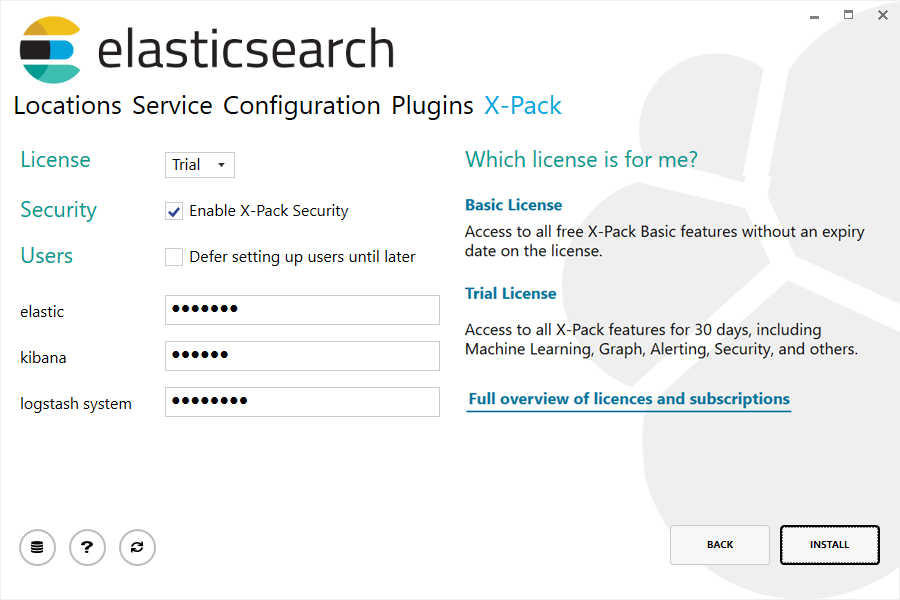
X-Pack 包含一个 Trail(试用)或 基本(Basic)许可证。 Trail(试用)许可证可以使用 30 天,之后你可以获得一个可用的订阅。 基本(Basic)许可证是永久免费的。 有关哪个许可证下有哪些可用的特性的更多信息,请参考 可用的订阅 页面。
点击安装按钮后,安装就开始了:
... 安装成功后会显示如下:

还可以从命令行执行 .msi 来安装 Elasticsearch。
使用与图形用户界面相同的默认值的最简单的安装是先进入下载目录,然后运行命令:
msiexec.exe /i elasticsearch-7.7.1.msi /qn
默认情况下,msiexec.exe 不会等到安装程序执行完成,因为它是运行在 Windows子系统下的。
要等待进程完成并确保 %ERRORLEVEL% 被相应地设置,建议使用 start /wait 创建一个进程并等待它退出。
start /wait msiexec.exe /i elasticsearch-7.7.1.msi /qn
与任意一个 MSI 安装包一样,安装过程的日志文件可以在%TEMP%目录中找到,随机生成的日志文件名遵循 MSI<random>.LOG 格式。
可以使用命令行参数 /l 显示日志文件的路径:
start /wait msiexec.exe /i elasticsearch-7.7.1.msi /qn /l install.log
可以使用下面的命令行来显示所有支持的 Windows Installer 的命令行参数:
msiexec.exe /help
...或者参考 Windows Installer开发套件命令行选项。
GUI 中显示的所有设置也可以作为命令行参数(在Windows Installer文档中称为properties)使用,这些参数可以传递给 msiexec.exe:
|
|
安装目录。
路径中最后一个目录 必须 是 Elasticsearch 的版本。
默认为 |
|
|
数据存储的目录。
默认为 |
|
|
配置存放的目录。
默认为 |
|
|
日志存放的目录。
默认为 |
|
|
数据、配置和日志目录是否应该创建在安装目录下。
默认 |
|
|
是否要将 Elasticsearch 安装并配置为 Windows 服务。
默认 |
|
|
是否在安装完成后启动 Windows 服务。默认 |
|
|
是否在 Windows 启动时启动 这个服务。
默认 |
|
|
安装的服务是否以本地系统账号(LocalSystem Account)运行。
默认 |
|
|
安装的服务是否以 网络服务账号(NetworkService Account)运行。
默认 |
|
|
安装的服务是否以 一个指定的已有的账号 运行。
默认 |
|
|
安装的Windows服务运行的账号名称。
默认为 |
|
|
安装的Windows服务运行的账号的密码。
默认为 |
|
|
集群名称。
默认为 |
|
|
节点名称。默认为 |
|
|
Elasticsearch 是否被配置为 主节点(master node)。
默认为 |
|
|
Elasticsearch 是否被配置为 数据节点(data node)。
默认为 |
|
|
Elasticsearch 是否被配置为 预处理节点(ingest node)。
默认 |
|
|
给 Elasticsearch 的 JVM 堆分配的内存大小。
默认 |
|
|
是否应该使用 |
|
|
用于 单播发现(unicast discovery) 的一个逗号分割的主机列表,格式为 |
|
|
为了形成集群,必须可见的符合主节点的最小节点数量。
默认为 |
|
|
绑定到此节点的主机名或IP地址,并会发布(publish)(公告,advertise)到集群中的其他节点的主机。
默认为 |
|
|
通过 HTTP 公开 Elasticsearch API 服务的端口。
默认为 |
|
|
集群的节点之间进行内部沟通的端口。
默认为 |
|
|
安装时选择要下载和安装的插件列表,以逗号分割。
默认为 |
|
|
下载插件时是用的 HTTPS 代理主机。
默认为 |
|
|
下载插件时是用的 HTTPS 代理的端口。
默认为 |
|
|
下载插件时是用的 HTTP 代理主机。
默认为 |
|
|
下载插件时是用的 HTTP 代理的端口。
默认为 |
|
|
要安装的许可证的类型, |
|
|
当使用 |
|
|
当安装时使用 |
|
|
当安装时使用 |
|
|
当安装时使用 |
|
|
当安装时使用 |
|
|
当安装时使用 |
要传递一个值,可以简单的按 <PROPERTYNAME>="<VALUE>" 格式把属性名称及其值附加到安装命令上。
比如,要使用不同于默认安装目录的安装目录:
start /wait msiexec.exe /i elasticsearch-7.7.1.msi /qn INSTALLDIR="C:\Custom Install Directory{version}"
有关包含引号的值的其他规则,参考 Windows Installer SDK 命令行选项。
一些商业特性会自动在 Elasticearch 中创建索引。
默认情况下,Elasticsearch 被配置为允许自动创建索引,并且不需要其他步骤。
但是,如果在 Elasticsearch 中禁用了自动索引创建,则必须在 elasticsearch.yml 文件中配置 action.auto_create_index,以允许商业特性创建以下索引:
action.auto_create_index: .monitoring*,.watches,.triggered_watches,.watcher-history*,.ml*
安装好后,就可以从命令行启动 Elasticsearch;如果不是作为服务安装或未配置为安装完成时启动,可以这样操作:
.\bin\elasticsearch.exe
命令行终端会显示类似下面这样的信息:
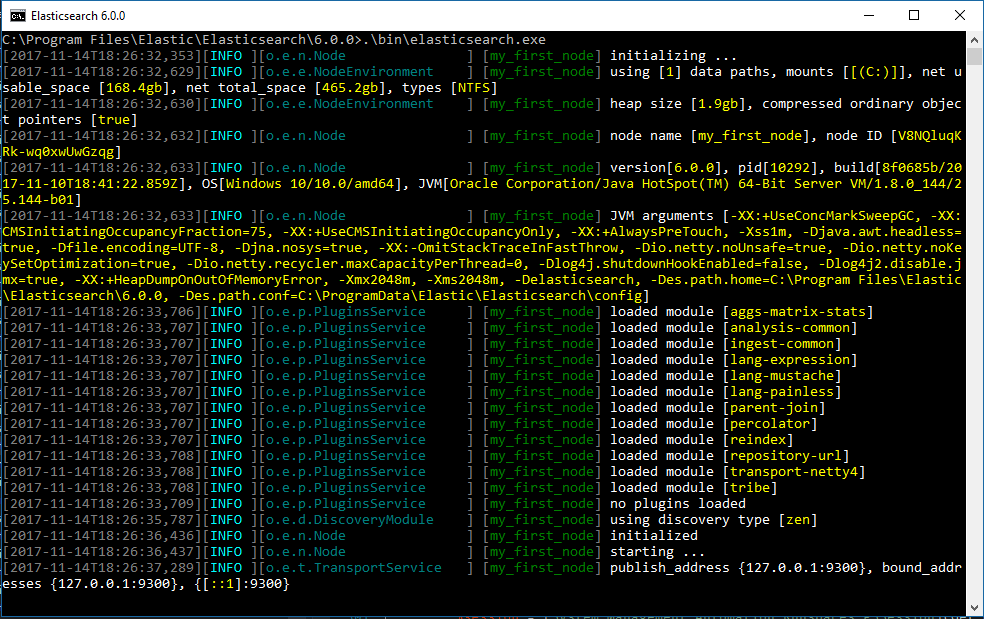
默认情况下,Elasticsearch 在前台运行,日志是打印到LOGSDIRECTORY目录下的文件名为 <cluster name>.log 的标准输出(STDOUT),并且可以通过按 Ctrl-C来停止运行。
Elasticsearch 默认从 %ES_PATH_CONF%\elasticsearch.yml 文件加载配置。
配置 Elasticsearch 中解释了此配置文件的格式。
任何一个可以在配置文件中指定的设置,都可以在命令行中使用-E语法指定,如下所示:
.\bin\elasticsearch.exe -E cluster.name=my_cluster -E node.name=node_1
包含空格的值必须用引号括起来。比如 -E path.logs="C:\My Logs\logs" 。
通常,任何集群范围的设置(如cluster.name)都应该添加到 elasticsearch.yml 配置文件中,而任何特定于节点的设置(如node.name)都可以在命令行中指定。
你可以通过向 localhost 上的端口 9200 发送一个 HTTP 请求来测试 Elasticsearch 节点是否正在运行:
GET /
应该会给你一个类似下面这样的响应:
{
"name" : "Cp8oag6",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "AT69_T_DTp-1qgIJlatQqA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.7.1",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "tar",
"build_hash" : "f27399d",
"build_date" : "2016-03-30T09:51:41.449Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.5.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "1.2.3",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "1.2.3"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Elasticsearch可以作为服务安装在后台运行,也可以在启动时自动启动,无需任何用户交互。 这可以通过在安装时使用以下命令行选项来实现:
-
INSTALLASSERVICE=true -
STARTAFTERINSTALL=true -
STARTWHENWINDOWSSTARTS=true
安装好后,Elasticsearch 就会出现的服务控制面板中:
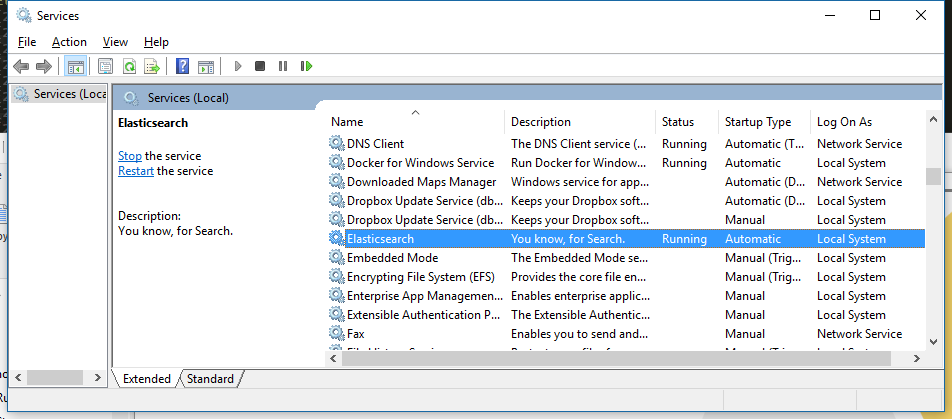
且可以通过控制面板来停止和重启,或者像下面这样从命令行操作:
使用命令行提示符:
sc.exe stop Elasticsearch sc.exe start Elasticsearch
使用 PowerShell:
Get-Service Elasticsearch | Stop-Service Get-Service Elasticsearch | Start-Service
在服务安装后,可以通过jvm.options 和 配置文件 elasticsearch.yml 来修改设置。
大多数修改(比如 JVM 设置)需要重启服务才能生效。
.msi 安装包支持升级一个已安装的版本到新的版本。
在通过 GUI 升级的过程中,它会处理所有已安装插件的升级,并保留你的数据和配置。
下载并双击新版本的 .msi 安装包,就会启动 GUI 安装向导。
第一步会列出之前已安装版本的只读选项:
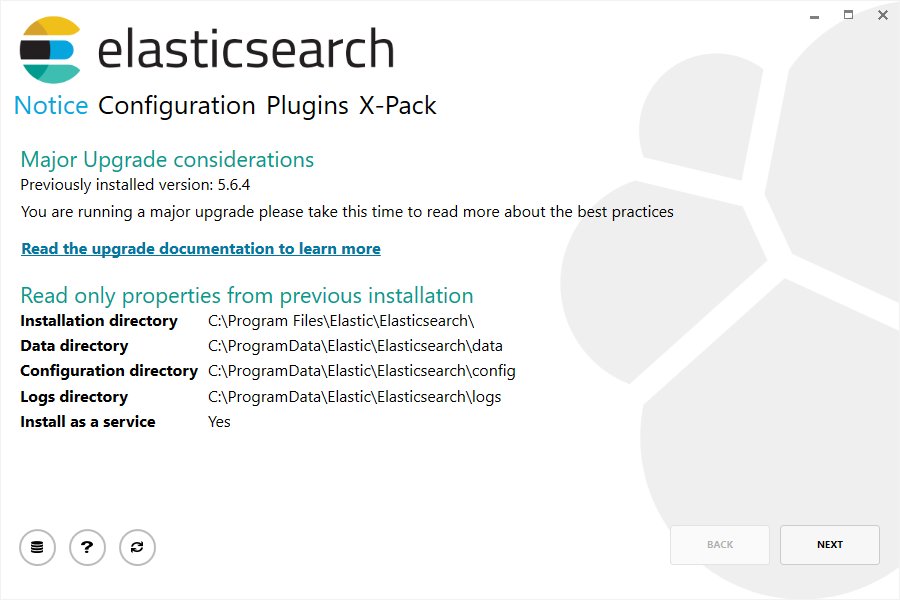
下一步会允许你修改部分配置选项:
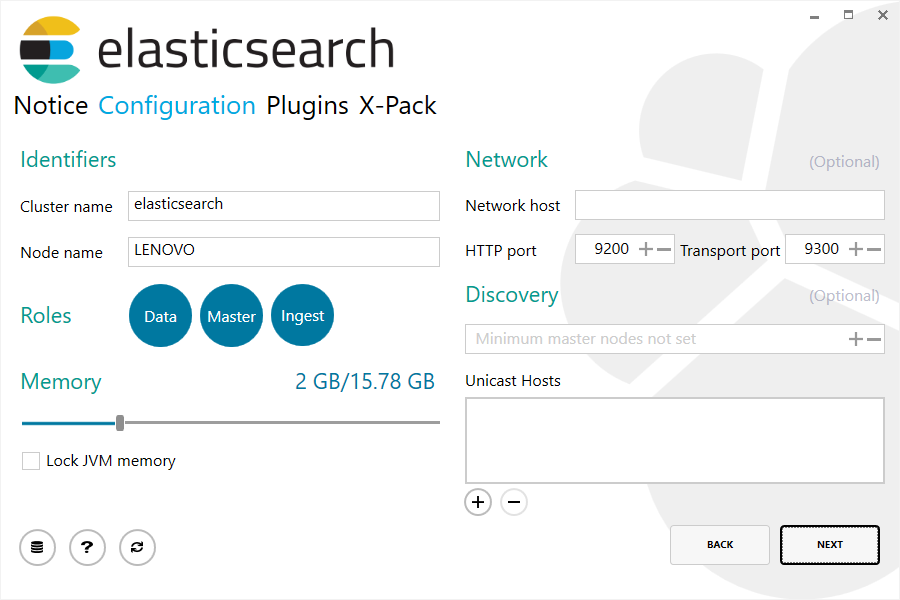
最后,插件操作步骤中允许你将已安装的插件升级或者移除,对于尚未安装的插件,可以下载并安装:
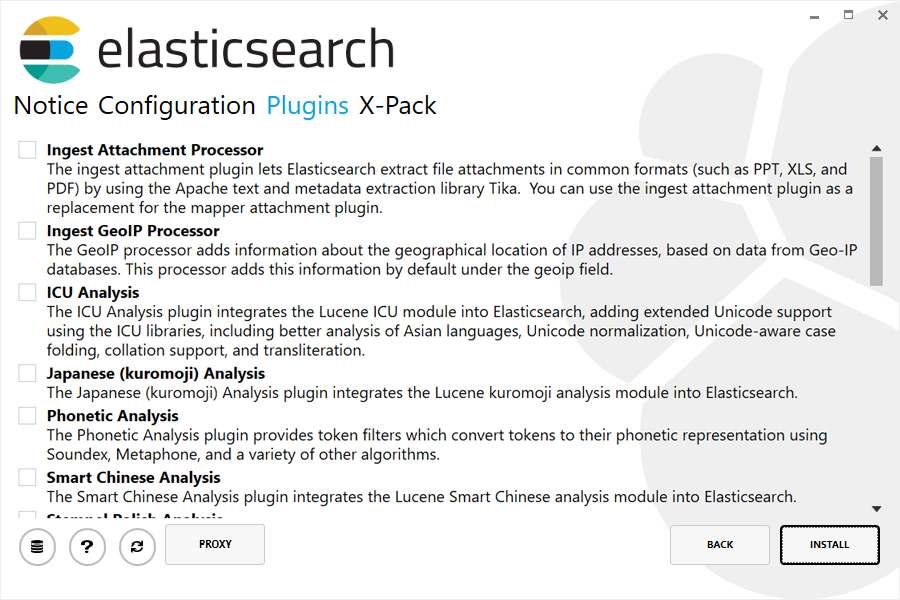
.msi 安装包还可以使用命令行来升级 Elasticsearch。
命令行升级需要传递与首次安装时 相同的 命令行属性;Windows 安装程序不会记住这些属性。
比如,如果你之前是以命令行选项 PLUGINS="ingest-geoip" 和 LOCKMEMORY="true" 来安装的,那么你从命令行执行升级时必须传递相同的值。
参数 INSTALLDIR(如果原来指定了) 是一个例外,这各值必须使用与当前安装版本不同的目录。
如果指定了 INSTALLDIR,路径的最后一个目录 必须 包含必须是版本号,比如:
C:\Program Files\Elastic\Elasticsearch\7.7.1
最简单的升级方式是,假设 Elasticsearch 是使用所有的默认值安装的,首先导航到下载目录,然后运行:
start /wait msiexec.exe /i elasticsearch-7.7.1.msi /qn
与安装过程类似,可以通过命令行参数 /l 来指定升级过程的日志存放的路径:
start /wait msiexec.exe /i elasticsearch-7.7.1.msi /qn /l upgrade.log
.msi 安装包处理安装时建立的所有文件夹和文件夹的卸载工作。
卸载程序会移除安装时建立的 所有 内容, 除了 数据、配置和日志目录。 建议在升级前给数据目录做个备份,或者使用 快照(snapshot) API。
MSI 安装包没有提供卸载的 GUI。
已安装的程序,可以通过按 Windows 徽标键然后输入 添加或删除程序 来打开设置管理。
打开后,在已安装应用的列表中找到 Elasticsearch,点击并选择 卸载:
这将启动卸载程序。
卸载 ElasticSearch 还可以使用命令, 先切换到包含 .msi 安装包的目录,然后执行:
start /wait msiexec.exe /x elasticsearch-7.7.1.msi /qn
与安装过程类似,可以通过命令行参数 /l 来指定卸载过程的日志存放的路径:
start /wait msiexec.exe /x elasticsearch-7.7.1.msi /qn /l uninstall.log
你现在已经设置了一个 Elasticsearch 测试环境。 在开始正式开发或开始使用 Elasticsearch 进行生产之前,你还必须做一些额外的设置:
- 学习如何 配置 Elasticsearch。
- 配置 重要的 Elasticsearch 设置。
- 配置 重要的系统设置。