本地英文版地址: ../en/zip-windows.html
在Windows上可以使用 Windows 的 .zip 归档来安装 Elasticsearch。
这带有一个 elasticsearch-service.bat 命令,该命令将设置 Elasticsearch 作为服务运行。
在Windows上,Elasticsearch 一直使用 .zip 归档来安装。
一个 MSI安装包 为Windows提供了最简单的上入门体验。
如果你愿意,你可以继续使用 .zip 方法。
此软件包可在 Elastic 许可下免费使用。 它包含开放源码和免费的商业特性,并能访问付费商业特性。 开始为期30天的试用 尝试使用付费的商业特性。 有关 Elastic 许可等级的更多信息,请参考 订阅(Subscriptions) 页面。
在Windows上,Elasticsearch 的机器学习特性需要 Microsoft Universal C Runtime 库。 这个库内置在 Windows10, Windows Server 2016 以及更近期的Windows版本。 对于更老版本的Windows,可以通过 Windows Update安装,或者 单独下载 页面。 如果你无法安装 Microsoft Universal C Runtime 库,只要你停用机器学习特性,你仍然可以使用Elasticsearch的其他功能。
Elasticsearch 最新的稳定版本可以在 下载 Elasticsearch 页面找到。 其他版本可以在 过去发布的版本(Past Releases) 页面上找到。
从 https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.7.1-windows-x86_64.zip 下载 lasticsearch v7.7.1 版本的 .zip 归档。
或者,你也可以下载这个安装包,其中只包含Apache2.0许可代码:https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss-7.7.1-windows-x86_64.zip
使用你喜欢的解压工具解压它。
这会建立一个名为 elasticsearch-7.7.1 的文件夹,并称其为 %ES_HOME%。
在终端窗口中,cd 到 %ES_HOME% 目录,比如:
cd c:\elasticsearch-7.7.1
一些商业特性会自动在 Elasticearch 中创建索引。
默认情况下,Elasticsearch 被配置为允许自动创建索引,并且不需要其他步骤。
但是,如果在 Elasticsearch 中禁用了自动索引创建,则必须在 elasticsearch.yml 文件中配置 action.auto_create_index,以允许商业特性创建以下索引:
action.auto_create_index: .monitoring*,.watches,.triggered_watches,.watcher-history*,.ml*
Elasticsearch 可以像下面这样从命令行启动:
.\bin\elasticsearch.bat
如果你有密码保护的 ElasticSearch 密钥存储库,系统将提示你输入密钥存储库的密码。 更多信息参考 安全设置。
默认情况下,Elasticsearch 在前台运行,日志是打印到标准输出(STDOUT)的,并且可以通过按 Ctrl-C来停止运行。
Elasticsearch 默认从 %ES_HOME%\config\elasticsearch.yml 文件加载配置。
配置 Elasticsearch 中解释了此配置文件的格式。
任何一个可以在配置文件中指定的设置,都可以在命令行中使用-E语法指定,如下所示:
.\bin\elasticsearch.bat -Ecluster.name=my_cluster -Enode.name=node_1
包含空格的值必须用引号括起来。比如 -E path.logs="C:\My Logs\logs" 。
通常,任何集群范围的设置(如cluster.name)都应该添加到 elasticsearch.yml 配置文件中,而任何特定于节点的设置(如node.name)都可以在命令行中指定。
你可以通过向 localhost 上的端口 9200 发送一个 HTTP 请求来测试 Elasticsearch 节点是否正在运行:
GET /
应该会给你一个类似下面这样的响应:
{
"name" : "Cp8oag6",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "AT69_T_DTp-1qgIJlatQqA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.7.1",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "tar",
"build_hash" : "f27399d",
"build_date" : "2016-03-30T09:51:41.449Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.5.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "1.2.3",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "1.2.3"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Elasticsearch可以作为服务安装在后台运行,也可以在启动时自动启动,无需任何用户交互。
这可以通过bin\文件夹中的elasticsearch-service.bat脚本来实现,该脚本允许用户安装、删除、管理或配置服务,并可能启动和停止服务,所有这些都可以从命令行完成。
c:\elasticsearch-7.7.1\bin>elasticsearch-service.bat Usage: elasticsearch-service.bat install|remove|start|stop|manager [SERVICE_ID]
该脚本需要一个参数(要执行的命令),后跟一个指示服务id的可选参数(在安装多个 Elasticsearch 服务时很有用)。
可用的命令如下:
|
|
安装Elasticsearch为服务 |
|
|
移除已安装的 Elasticsearch 服务(如果已经启动了则停止服务) |
|
|
启动 Elasticsearch 服务(如果已安装) |
|
|
停止 Elasticsearch 服务(如果已启动) |
|
|
启动一个管理已安装服务的GUI |
服务名称及 JAVA_HOME 的值会在安装过程中给出:
c:\elasticsearch-7.7.1\bin>elasticsearch-service.bat install Installing service : "elasticsearch-service-x64" Using JAVA_HOME (64-bit): "c:\jvm\jdk1.8" The service 'elasticsearch-service-x64' has been installed.
虽然 JRE 可以用于 Elasticsearch 服务,但由于它使用客户端虚拟机(而不是为长时间运行的应用程序提供更好性能的服务端 JVM),因此不鼓励使用它,并将发出警告。
系统环境变量 JAVA_HOME 应该设置为你希望服务使用的 JDK 安装的路径。
如果升级了 JDK,不需要重新安装服务,但是你必须设置系统环境变量 JAVA_HOME 的路径为新的 JDK 的安装路径。
但是,不支持跨 JVM 类型升级(例如,JRE 与 SE),并且确实需要重新安装服务。
自定义服务设置
Elasticsearch 服务可以在安装前通过设置以下环境变量进行配置(使用命令行中的set 命令,或通过 系统属性->环境变量 图形用户界面)。
|
|
服务的唯一标识符。
如果在一个机器上安装多个实例,则非常有用。
默认值为 |
|
|
运行时使用的用户,默认为本地系统账号。 |
|
|
用户 |
|
|
服务名称。默认值为 |
|
|
服务描述。默认为 |
|
|
运行服务所需的JVM的安装目录。 |
|
|
服务日志的目录,默认为 |
|
|
配置文件的目录(它必须包含 |
|
|
你可能希望应用的任何其他 JVM 系统属性。 |
|
|
服务的启动模式。可以是 |
|
|
procrun 等待服务正常退出的超时时间(单位:秒)。默认值为 |
At its core, elasticsearch-service.bat relies on Apache Commons Daemon project to install the service.
作为它的核心,elasticsearch-service.bat 依赖 Apache Commons Daemon 项目来安装该服务。
服务安装前设置的环境变量将被复制,并将应用在服务的生命周期中。
这意味着,除非重新安装服务,否则安装后对它们所做的任何更改都不会被接受。
在Windows上,当从命令行运行 Elasticsearch,或者第一次将 Elasticsearch 作为服务安装时,堆内存大小可以像任何其他 Elasticsearch 安装一样进行配置。
要调整已安装服务的堆内存大小,请使用服务管理器:bin\elasticsearch-service.bat manager.
该服务会自动配置一个私有临时目录,供 Elasticsearch 运行时使用。
该私有临时目录被配置为运行安装的用户的私有临时目录的子目录。
如果服务将在不同的用户下运行,你可以在执行服务安装之前将环境变量ES_TMPDIR设置为首选位置来配置服务应该使用的临时目录的位置。
- 使用管理器的图形用户界面
-
你还可以使用管理器的图形用户界面(
elasticsearch-service-mgr.exe)在服务安装后去配置服务,这个界面提供了对已安装服务的详细信息,包括服务的状态、启动类型、JVM、启动和停止设置等。 只需从命令行调用elasticsearch-service.bat manager就能打开管理器窗口:
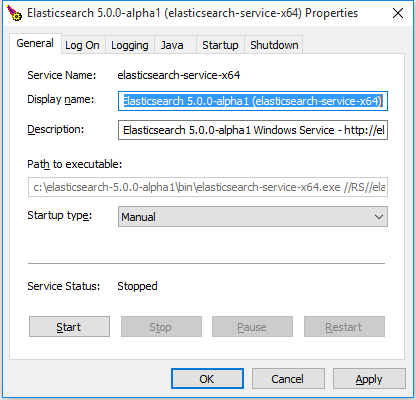
使用管理器的图形用户界面进行的大多数修改(比如 JVM设置)需要重启服务才能生效。
.zip 安装包是完全独立的。
默认情况下,所有的文件和目录,都包含在解压归档文件时创建的 $ES_HOME 目录中。
这是很方便的,因为你不需要创建任何目录就可以开始使用 Elasticsearch,而卸载 Elasticsearch 就像删除 $ES_HOME 目录一样简单。
但是,建议更改配置目录、数据目录和日志目录的默认位置,以便以后不会因为不小心而删除了重要数据。
| 类型 | 描述 | 默认位置 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|---|
home |
Elasticsearch的主目录或 |
解压归档文件时创建的目录 |
|
bin |
二进制脚本,包含启动一个节点的 |
|
|
conf |
包含 |
|
|
data |
节点上的每个索引/分片的数据文件的位置。 可以设置多个位置。 |
|
|
logs |
日志文件的存放位置 |
|
|
plugins |
插件文件的存放位置。每个插件都放在一个子文件夹中。 |
|
|
repo |
共享的文件系统存储库的位置。 可以设置多个位置。 可以将文件系统存储库放置到此处指定的任何目录的任何子目录中。 |
未配置 |
|
你现在已经设置了一个 Elasticsearch 测试环境。 在开始正式开发或开始使用 Elasticsearch 进行生产之前,你还必须做一些额外的设置:
- 学习如何 配置 Elasticsearch。
- 配置 重要的 Elasticsearch 设置。
- 配置 重要的系统设置。