本地英文版地址: ../en/get-started-roles.html
Assign rolesedit
By default, all users can change their own passwords, get information about
themselves, and run the authenticate API. If you want them to do more than
that, you need to give them one or more roles.
Each role defines a specific set of actions (such as read, create, or delete) that can be performed on specific secured resources (such as indices, aliases, documents, fields, or clusters). To help you get up and running, there are built-in roles.
Go to the Management / Security / Roles page to see them:

Select a role to see more information about its privileges. For example, select
the kibana_system role to see its list of cluster and index privileges. To
learn more, see Indices privileges.
Let’s assign the kibana_admin role to your user. Go back to the
Management / Security / Users page and select your user. Add the kibana_admin
role and save the change. For example:

This user now has administrative access to all features in Kibana. For more information about granting access to Kibana see Kibana authorization.
If you completed all of the steps in Getting started with the Elastic Stack, you should have Metricbeat data stored in Elasticsearch. Let’s create two roles that grant different levels of access to that data.
Go to the Management / Security / Roles page and click Create role.
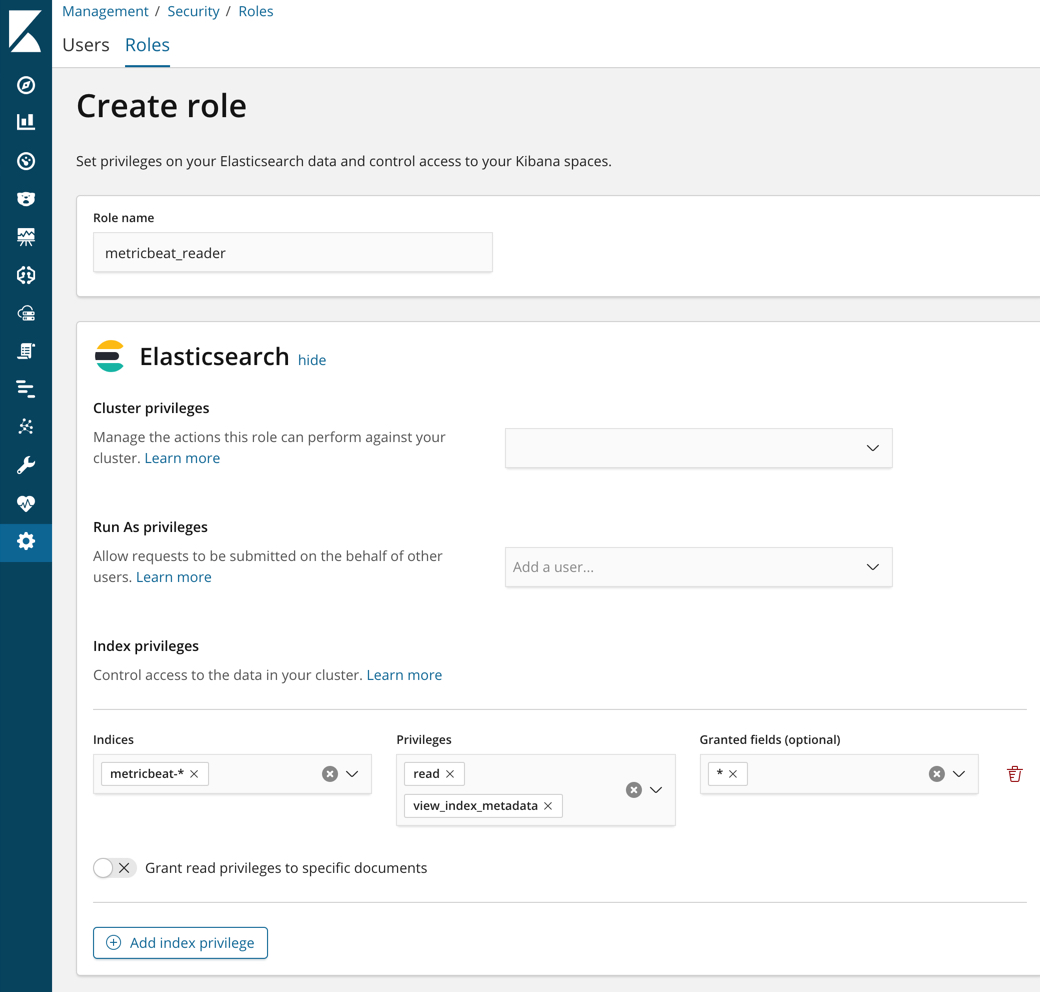
Create a metricbeat_reader role that has read and view_index_metadata
privileges on the metricbeat-* indices:
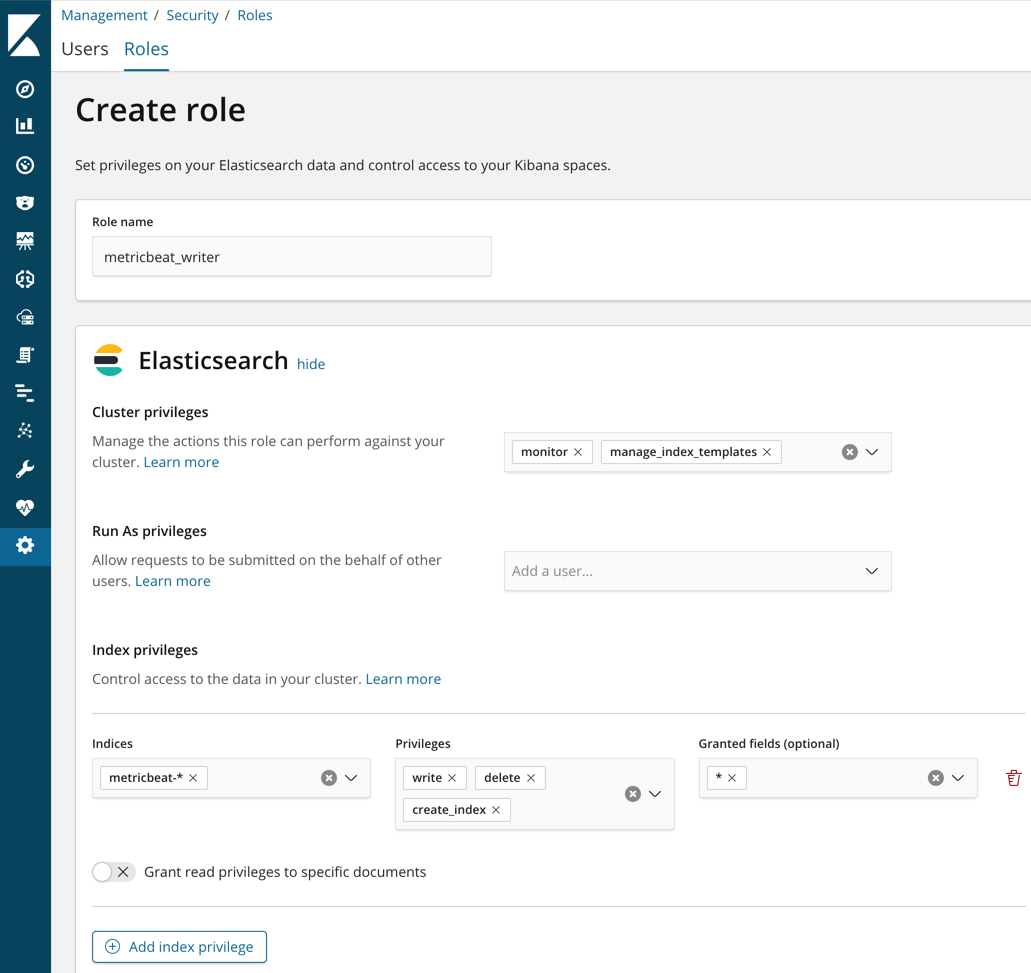
Create a metricbeat_writer role that has manage_index_templates and monitor
cluster privileges, as well as write, delete, and create_index privileges
on the metricbeat-* indices:
Now go back to the Management / Security / Users page and assign these roles
to the appropriate users. Assign the metricbeat_reader role to your personal
user. Assign the metricbeat_writer role to the logstash_internal user.
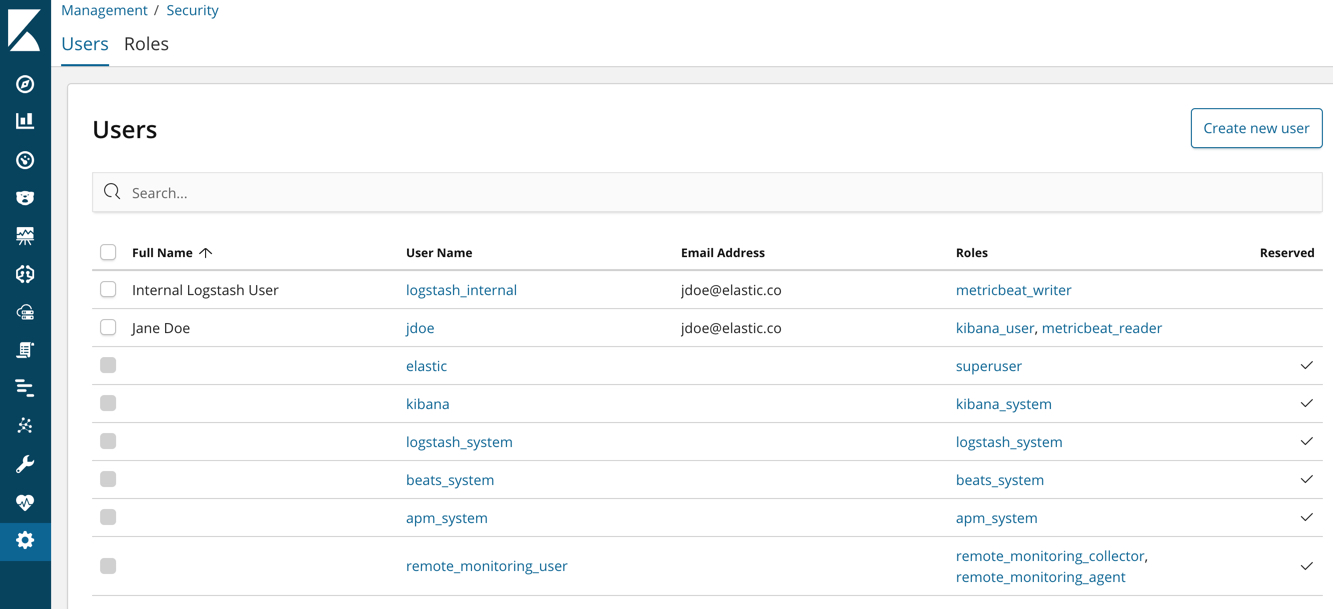
The list of users should now contain all of the built-in users as well as the two you created. It should also show the appropriate roles for your users:
If you want to learn more about authorization and roles, see User authorization.